
#Cloudwatch logs full
SenseDeep supports infinite scrolling through log data with powerful full text searching. It has real-time live-tailing of events, smooth scrolling, rapid navigation and instant queries. Learn AWS For The Real World - Not For Certifications. Log Groups hold all logs for one application or service. Log Streams contain one or more log events. Log Events are the actual text outputs of your application. CloudWatch follows the concepts of Log Streams, Groups, and Events. SenseDeep aggregates logs from multiple AWS log streams into a single, uniform view for analysis. Logs are text outputs of your application.
#Cloudwatch logs manual
You can click on a link to pull more events, but the display will not automatically display new log events without manual intervention. The CWL Log viewer provides a static paged view of events. The Viewer does not automatically refresh the log view when new events arrive.While there is an API to aggregate events (filterLogEvents), CWL does not provide a unified view of a log file. The streams are presented as discrete files that you need to examine one by one. AWS will typically create new log streams when an existing stream gets over a certain size, or services are restarted, so streams tend to multiply.

Select Insights under Logs and then choose your log group.
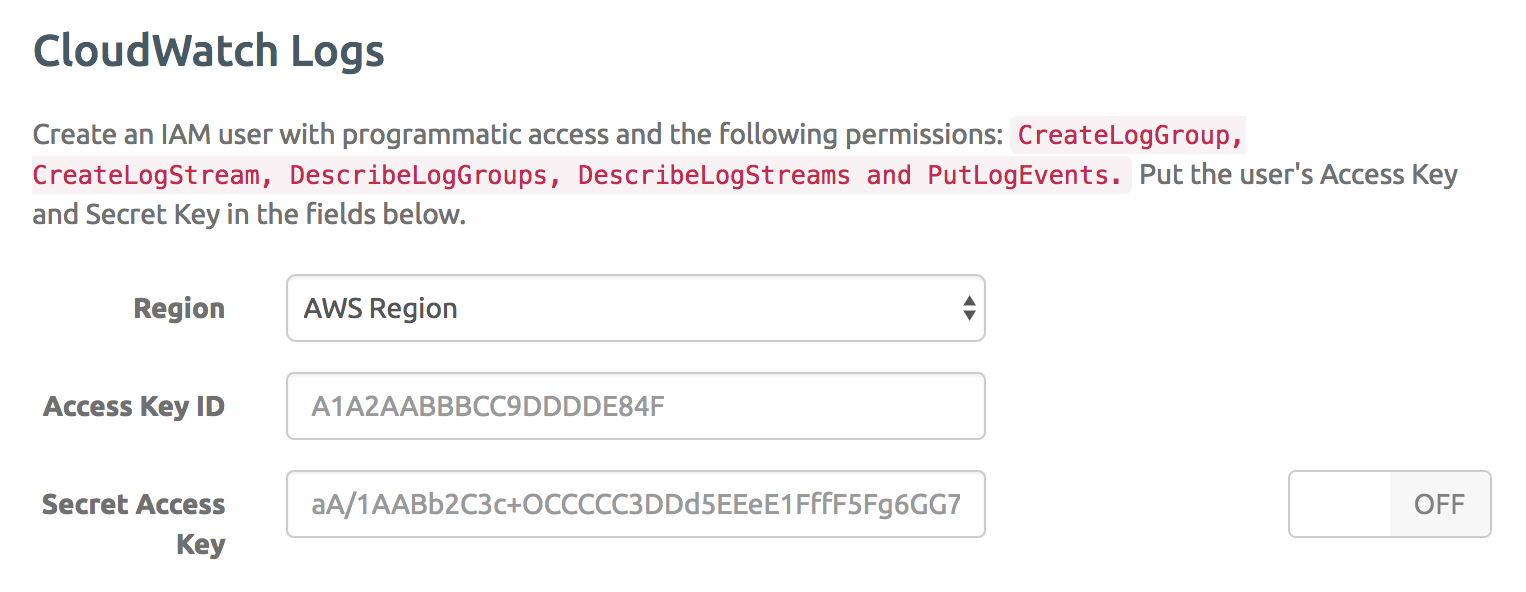
CloudWatch Logs also supports aws:SourceArn and aws:SourceAccount condition context keys. Replace 'logArn' with the ARN of your CloudWatch Logs resource, such as a log group or log stream. By using the CloudWatch Logs Insights we can get AWS to do all the heavy lifting for us. The following example creates a resource policy enabling the Route 53 service to put DNS query logs in to the specified log group. While using the console is a good start, we can do better. CWL Logs are comprised of one or more log streams that are logically represent a single log. CloudWatch Logs Here’s what the raw flow log data looks like in a CloudWatch Log group. The CWL Viewer does not automatically aggregate log streams.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
